
3.3 Coping with uncertainty, ambiguity & risk
COU_6_EN
Title
3.3 Coping with uncertainty, ambiguity & risk
Keywords
• Uncertainty •Ambiguity • Risk
Author
DELTA
Languages
English
Objectives/goals
• The training participant will learn what is the meaning of the distinction in uncertainty, ambiguity & risk in business
• The participant will be able to verify his business with uncertainty, ambiguity & risk
• The participant will be aware that each business is associated with uncertainty and risk not only in its creation and operation
Contents
Coping with uncertainty, ambiguity and risk
A Introduction and basics
What do we mean with risk?
Uncertainty, ambiguity and risk in business are the basic barriers or challanges to the development of any enterprise or business. The ability to deal with it is crucial for business development, increasing profits and in many cases also survival in the market.
At the stage of establishing the enterprise, a SWOT analysis (strengths and weaknesses, opportunities and threats) is created. Once the business is up and running, dealing with incompetence, ambiguity and risk is a key part of management.
|
Seeking definitions
•Uuncertainty (in Business) a situation, in which the probability distribution is unknown (i.e. something that can be understood in more than one way or can have more than one outcome)
•Risk refers to the probability or threat of loss, liability, injury, damage, or any other negative occurrence resulting from external or internal vulnerabilities, and that may be prevented or avoided through preventive action
|
To resume
In order to obtain the full picture of uncertainty and ambiguity, we can make a comparison with understanding certainty:

|
Obstacles in doing business pt.1
|
Barriers in doing business
|
|
Barriers to entry is an economics and business term describing factors that can prevent or impede newcomers into a market or industry sector, and so limit competition. These can include high start-up costs, regulatory hurdles, or other obstacles that prevent new competitors from easily entering a business sector
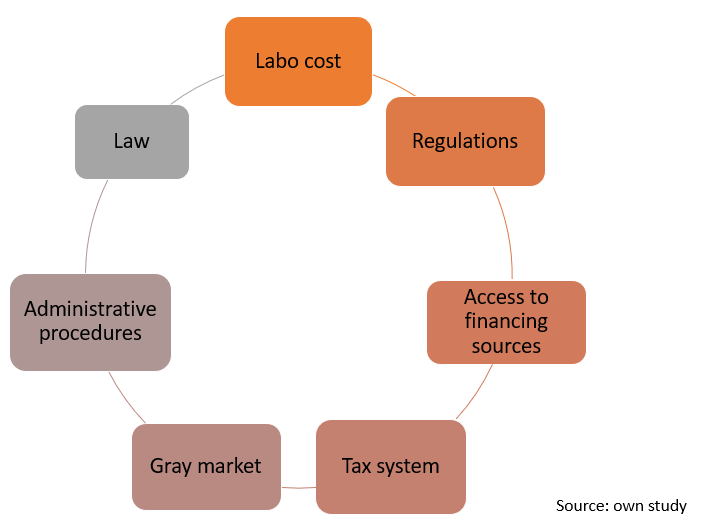
|
|
Obstacles in doing business pt.2
Obstacles in doing business pt.3
A SWOT Analysis perspective
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a technique for assessing these four aspects of your business.
Conducting a SWOT analysis is a powerful way to evaluate your company or project.
The primary objective of a SWOT analysis is to help organizations develop a full awareness of all the factors involved in making a business decision.

|
The decision-making process
Effective decision making
Decision making is a vital component of small business success.
Decisions based on a foundation of knowledge and sound reasoning can lead the company into long-term prosperity; conversely, decisions made on the basis of flawed logic, emotionalism, or incomplete information can quickly put a small business out of commission.
|
7 Characteristics of a Good Decision
1.An appropriate decision frame
2.Clear values to adhere to and objectives you are trying to accomplish
3.Creative alternatives to choose from
4.Good information
5.Clear tradeoffs and sound reasoning
6.Choice alignment with values and objectives
7.Committed implementation
|
7 Ways to deal with uncertainty
1.Replace expectations with plans
2.Prepare for different possibilities
3.Become a feeling observer
4.Get confident about your coping and adapting skills
5.Utilize stress reduction techniques pre-emptively
6.Focus on what you can control
7.Practice mindfulness
According to Lori Deschene
|
Moreover
Uncertainty is the only certainty there is, and knowing how to live with insecurity is the only security
John Allen Paulos
|
The words of the experts
Below are three examples of authors who point out mistakes made when making decisions. On this basis, try to compile your list of mistakes made when making decisions

|
The power of trust
Trust is the foundation and stimulus for every activity in the organization, it gives a sense of security and allows you to quickly react to changes in the environment.
There are eight Pillars of Trust (according to Business strategist David Horsager):
•Clarity – People trust the clear and mistrust the ambiguous
•Compassion – People put faith in those who care beyond themselves
•Character – People notice those who do what is right over what is easy
•Competency – People have confidence in those who stay fresh, relevant, and capable
•Commitment – People believe in those who stand through adversity
•Connection – People want to follow, buy from, and be around friends
•Contribution – People immediately respond to results
•Consistency – People love to see the little things done consistently
|
How uncertainty works
At TEDxCanberra 2012, Nobel Prize for Physics recipient, Professor Brian Schmidt, provides a live, engaging and practical demonstration of just how uncertainty works in the real world (click the image for the video)

|
Risk in Business
Internal VS External risk
Business risks refers to the possibility of a commercial business making inadequate profits (or even losses) due to uncertainties.
Business risks can arise due to the influence by two major risks: internal risks (risks arising from the events taking place within the organization) and external risks (risks arising from the events taking place outside the organization).
|
Internal VS External risk: examples
What is Risk Management?
Risk management helps you make better business decisions. It involves reducing the things that could have a negative effect on your business.
For example, the reducing the risk of injury by through safety procedures.
|
How you can manage risk?
Before you decide what to do, you’ll need to work out what your risks are and which ones are most urgent

|
How the best do it...
•Jeff Bezos. If you choose to only do things that you know will work, you will leave many options on the table
•Richard Branson. You can be careful and try to avoid risks, but you can't protect yourself all the time
•Walt Disney. In my opinion, courage is the main quality of leadership. Usually it involves risk taking, especially in new ventures
•Mark Zuckerberg. The biggest risk is not taking any risks. In a rapidly changing world, the strategy that guarantees failure is not taking risks
•Henry Ford. No one can really guarantee the future. The best we can do is increase the chances, calculate the risks involved, assess our ability to deal with them, and execute our plans safely
|
...and the implication for business:
In short:

|
Suggestions for self-study
In this video, Andy Penaluna, Director of the International Institute for Creative Entrepreneurial Development (http://www.uwtsd.ac.uk/iiced) at the University of Wales Trinity Saint David, explains that students can be exposed to uncertain, ambiguous activities where things change, deadlines shifts and there are no clear instructions on what shall be done next. Being exposed to such situations allows them to develop strategies to cope and learn to flexibly adapt to changing environments.

|
To recap:
•Every business is associated with uncertainty, ambiguity & risk
•Be guided by your reason, experience, and intuition in making binding decisions
•You will never avoid situations in which you will make important decisions
•You can always consult someone, discuss the matter in the team, try to thoroughly investigate a given situation
•Everyone makes mistakes and you can make them
|
To recap: Checklist for self-check
Bibliography
- Paulina Major, Zaufanie jako strategia radzenia sobie z niepewnością i ryzykiem w przedsiębiorstwach realizujących projekty. Zeszyty Naukowe Politechniki Śląskiej, Seria: Organizacja i Zarządzanie z. 113, Zabrze 2017.
- Michał Dudziak, Ewa Szpakowska, Zarządzanie ryzykiem i niepewność w działalności gospodarczej : podejmowanie decyzji biznesowych (Risk Management and Uncertainty in Business : Business Decisions), Gdańsk 2013, http://zif.wzr.pl/pim/2013_1_1_9.pdf
- WDA Bryant, Kumar Ankit, Puneet Mahajan, Maneesh Dangi, Bryan D’Aguiar, and Uday Damodaran (Coordinator), Uncertainty, Ambiguity, and Financial Decision-Making, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0256090920140107 , 2014
- Ovidijus Jurevicius, Â SWOT Analysis - Do It Properly! https://strategicmanagementinsight.com/tools/swot-analysis-how-to-do-it.html
- Virtual Strategist (2008). SWOT analysis: How to perform one for your organization (VIDEO). Available at:Â http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GNXYI10Po6A
- Wikipedia (2013). SWOT analysis. Available at:Â http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SWOT_analysis
- Samuelson W. F., Marks S. G. (1998). Ekonomia menedżerska, Wydawnictwo PWE, Warszawa
- Rabihah Md.Sum RISK MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING, Sydney, 2019  https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Rabihah_Mdsum/publication/319272438_Risk_Management_Decision_Making/links/599fa185a6fdccf5941f8d27/Risk-Management-Decision-Making.pdf
- Enrico Zio and Nicola Pedroni, Risk-informed decision-making processes https://www.foncsi.org/fr/publications/cahiers-securite-industrielle/overview-of-risk-informed-decision-making-processes/CSI-RIDM.pdf
- https://ec.europa.eu/economy_finance/publications/economic_paper/2014/pdf/ecp532_en.pdf , Business Dynamics and Red Tape Barriers Daria Ciriaci, Economic Papers 532 | September 2014
- https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/32436/9781464814402.pdf
- Doing Business Comparing Business Regulation in 190 Economies 2020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3357789/ Â Coping with Complexity, Uncertainty and Ambiguity in Risk Governance: A Synthesis
- Pictures: pixaby and google photos
- Group decision making (SĹ‚awomir Wawak) [video],via
- https://youtu.be/9n6qz5Ls3rg
Training Fiche PPT:
COU_3_en3.3 Coping with risk (DELTA).pptx
Follow Us: 


Consortium Partners
This project has been funded with support from the European Commission. This web site and its contents reflects the views only of the authors,
and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the information contained therein.
Legal description – Creative Commons licensing:
The materials published on the EntreComp project website are classified as Open Educational Resources' (OER) and can be freely (without permission of their creators): downloaded, used, reused, copied, adapted, and shared by users, with information about the source of their origin.
| |















Title
3.3 Coping with uncertainty, ambiguity & risk
Keywords
• Uncertainty •Ambiguity • Risk
Author
DELTA
Languages
English
Coping with uncertainty, ambiguity and risk
A Introduction and basics
What do we mean with risk?
Uncertainty, ambiguity and risk in business are the basic barriers or challanges to the development of any enterprise or business. The ability to deal with it is crucial for business development, increasing profits and in many cases also survival in the market.
At the stage of establishing the enterprise, a SWOT analysis (strengths and weaknesses, opportunities and threats) is created. Once the business is up and running, dealing with incompetence, ambiguity and risk is a key part of management.
Seeking definitions
To resume
In order to obtain the full picture of uncertainty and ambiguity, we can make a comparison with understanding certainty:
Obstacles in doing business pt.1
Barriers in doing business
Barriers to entry is an economics and business term describing factors that can prevent or impede newcomers into a market or industry sector, and so limit competition. These can include high start-up costs, regulatory hurdles, or other obstacles that prevent new competitors from easily entering a business sector
Obstacles in doing business pt.2
Obstacles in doing business pt.3
A SWOT Analysis perspective
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a technique for assessing these four aspects of your business.
Conducting a SWOT analysis is a powerful way to evaluate your company or project.
The primary objective of a SWOT analysis is to help organizations develop a full awareness of all the factors involved in making a business decision.
The decision-making process
Effective decision making
Decision making is a vital component of small business success.
Decisions based on a foundation of knowledge and sound reasoning can lead the company into long-term prosperity; conversely, decisions made on the basis of flawed logic, emotionalism, or incomplete information can quickly put a small business out of commission.
7 Characteristics of a Good Decision
7 Ways to deal with uncertainty
According to Lori Deschene
Moreover
Uncertainty is the only certainty there is, and knowing how to live with insecurity is the only security
John Allen Paulos
The words of the experts
Below are three examples of authors who point out mistakes made when making decisions. On this basis, try to compile your list of mistakes made when making decisions
The power of trust
Trust is the foundation and stimulus for every activity in the organization, it gives a sense of security and allows you to quickly react to changes in the environment.
There are eight Pillars of Trust (according to Business strategist David Horsager):
How uncertainty works
At TEDxCanberra 2012, Nobel Prize for Physics recipient, Professor Brian Schmidt, provides a live, engaging and practical demonstration of just how uncertainty works in the real world (click the image for the video)
Risk in Business
Internal VS External risk
Business risks refers to the possibility of a commercial business making inadequate profits (or even losses) due to uncertainties.
Business risks can arise due to the influence by two major risks: internal risks (risks arising from the events taking place within the organization) and external risks (risks arising from the events taking place outside the organization).
Internal VS External risk: examples
What is Risk Management?
Risk management helps you make better business decisions. It involves reducing the things that could have a negative effect on your business.
For example, the reducing the risk of injury by through safety procedures.
How you can manage risk?
Before you decide what to do, you’ll need to work out what your risks are and which ones are most urgent
How the best do it...
...and the implication for business:
In short:
Suggestions for self-study
In this video, Andy Penaluna, Director of the International Institute for Creative Entrepreneurial Development (http://www.uwtsd.ac.uk/iiced) at the University of Wales Trinity Saint David, explains that students can be exposed to uncertain, ambiguous activities where things change, deadlines shifts and there are no clear instructions on what shall be done next. Being exposed to such situations allows them to develop strategies to cope and learn to flexibly adapt to changing environments.
To recap:
To recap: Checklist for self-check
Training Fiche PPT:
COU_3_en3.3 Coping with risk (DELTA).pptx